Questo numero della rivista ArchAlp riflette sul rapporto tra progetto di architettura e suo racconto testuale e narrativo. Prova a farlo in più modi: progettisti che raccontano una loro opera o gruppo di opere; saggisti e scrittori, quindi non necessariamente architetti, che narrano una costruzione per loro particolarmente importante e significativa; o ancora – a cura della redazione della rivista – la ripresa di testi di progettisti del Novecento.
Obiettivo degli scritti – e quindi dell’intero numero – è quindi quello di fuoriuscire da una mera descrizione funzionale e tecnica dell’edificio, per ragionare sul nesso relazionale tra opera costruita e modalità della sua narrazione testuale. Opera e testo quindi come una sorta di “microcosmo”, che consente di riflettere sul rapporto della singola costruzione con il contesto alpino, con la storia e con le tecniche, mettendone in luce la peculiare “idea di architettura” di montagna. Ma non solo. Molto si è discusso in anni recenti sui rapporti di dipendenza e autonomia dei testi dedicati a una propria opera architettonica da parte di diversi autori della modernità. Da semplice testo descrittivo del progetto, la pagina scritta può trasformarsi in operazione che muovendo dal pretesto dell’opera diviene teoria, o ancora in metatesto che trascende gli oggetti per affermare una propria dimensione autonoma.
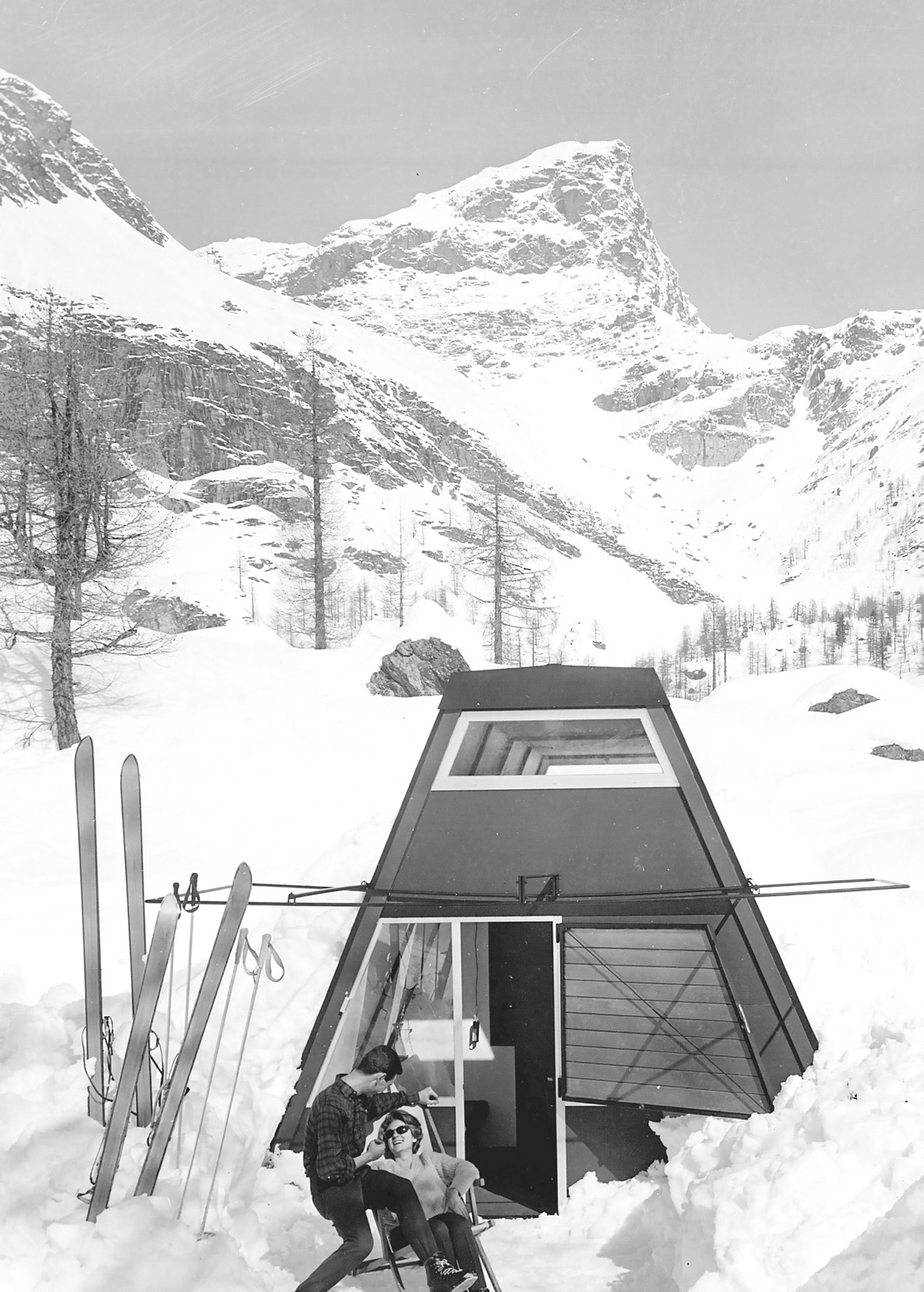
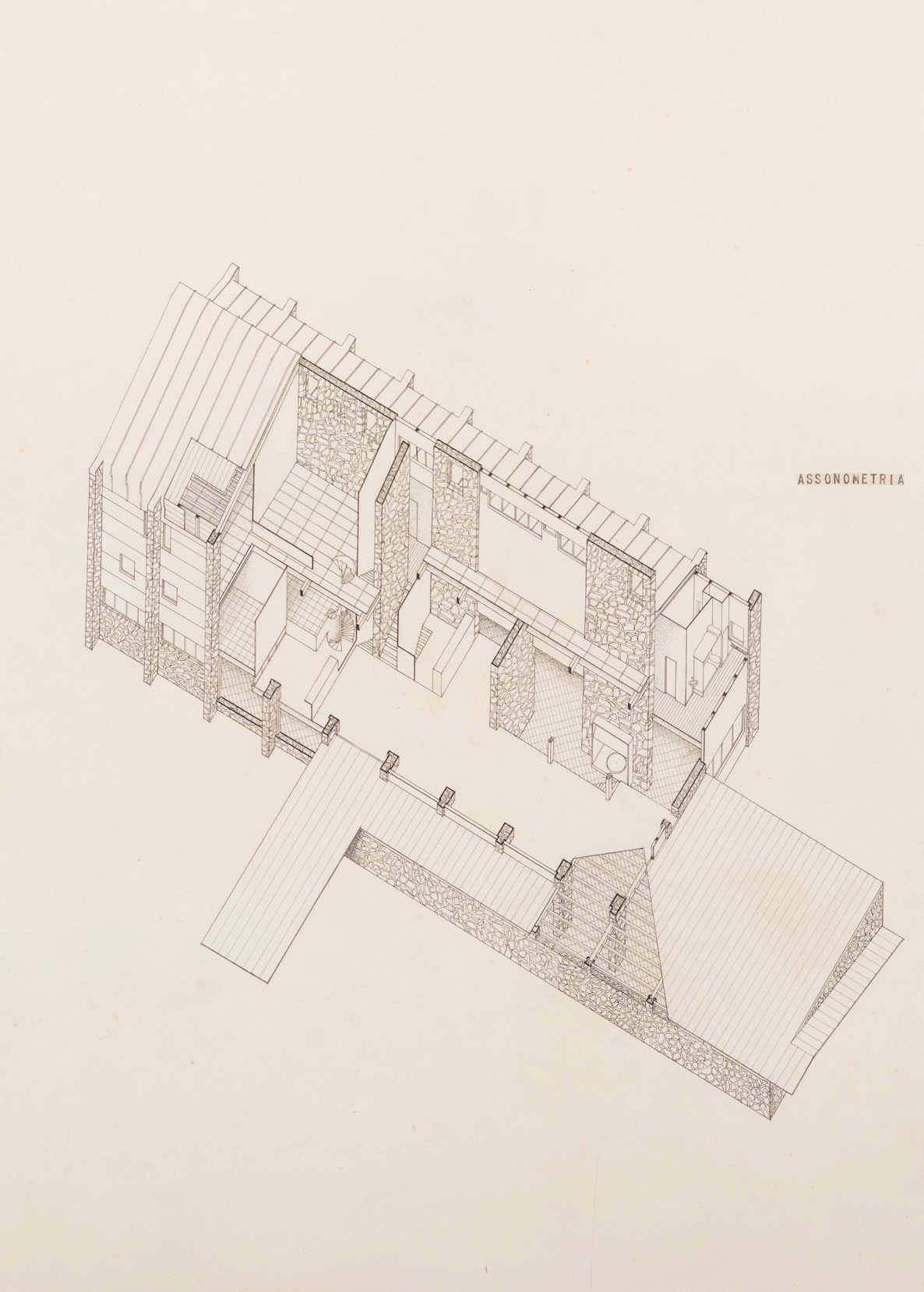
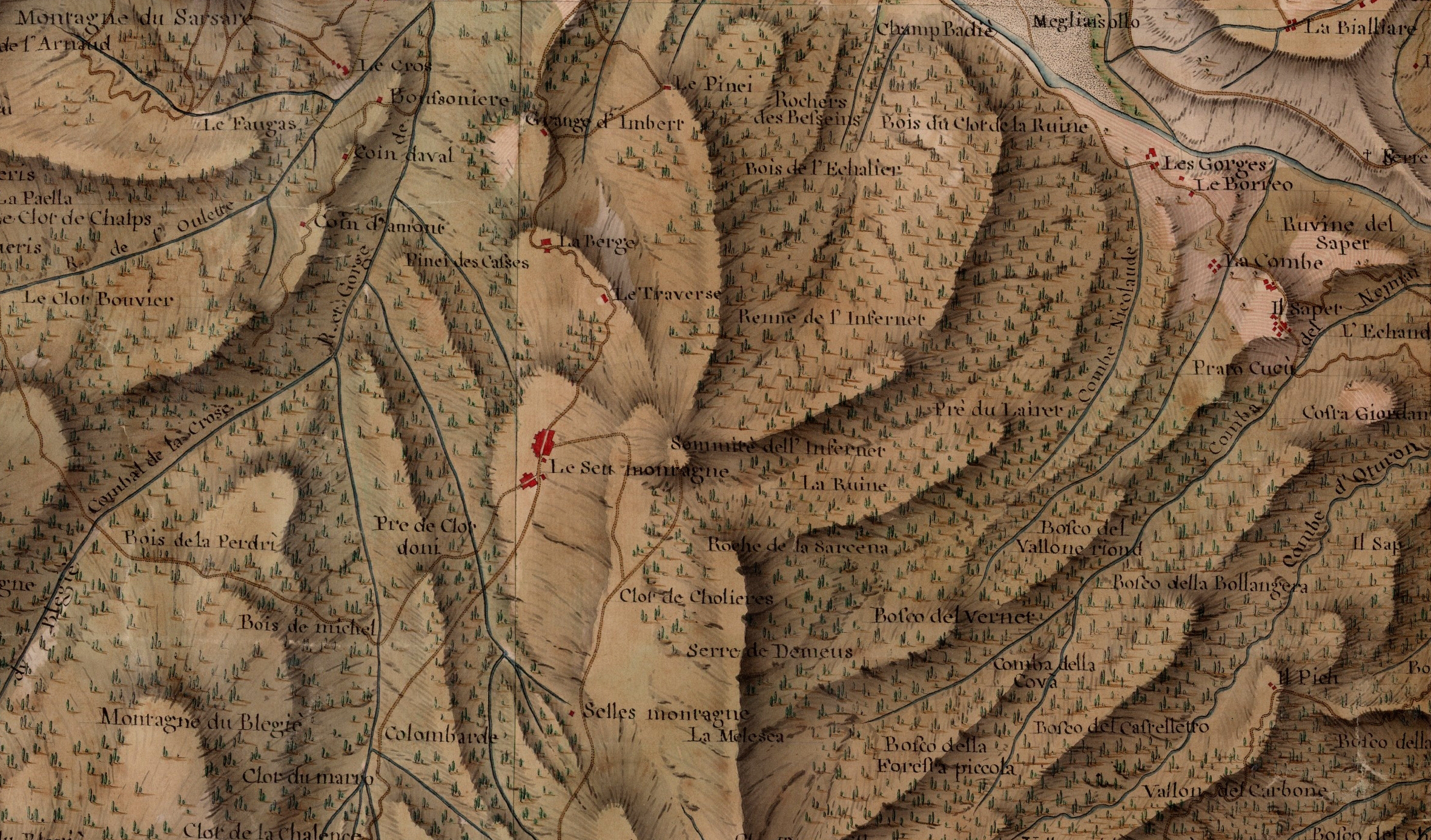
Il testo Tabù e tradizione nella costruzione montana di Carlo Mollino, pubblicato nel 1954 e riportato non a caso nelle prime pagine di questo numero, è considerato come uno dei principali testi, quasi un manifesto, dedicati dalla cultura architettonica al progetto in ambiente alpino. È interessante osservare come questo scritto venga a costruire delle immagini, delle metafore e dei sillogismi che a settant’anni di distanza rappresentano una sorta di patrimonio genetico dei modi con cui l’architettura guarda alle montagne e al loro progetto. Un testo che ha valenze inaugurali, e che edifica un “campo” dai precisi contenuti e contorni. Le pagine che seguono sono organizzate in due sezioni. La prima contiene testi di scrittori, storici, critici, architetti che parlano di progetti altrui. L’articolo di Enrico Camanni, scrittore di montagna, è notevole nel sapere ricreare quella Stimmung e Hybris che intesseva la modernità del secondo Novecento sulle Alpi italiane del turismo di massa. E poi ci sono le storie, tutt’altro che scontate, della Haus Böhler di Heinrich Tessenow e della Capanna Monolina, fino a quel progetto quasi inedito di Gianni Albricci e Marco Zanuso del 1938.
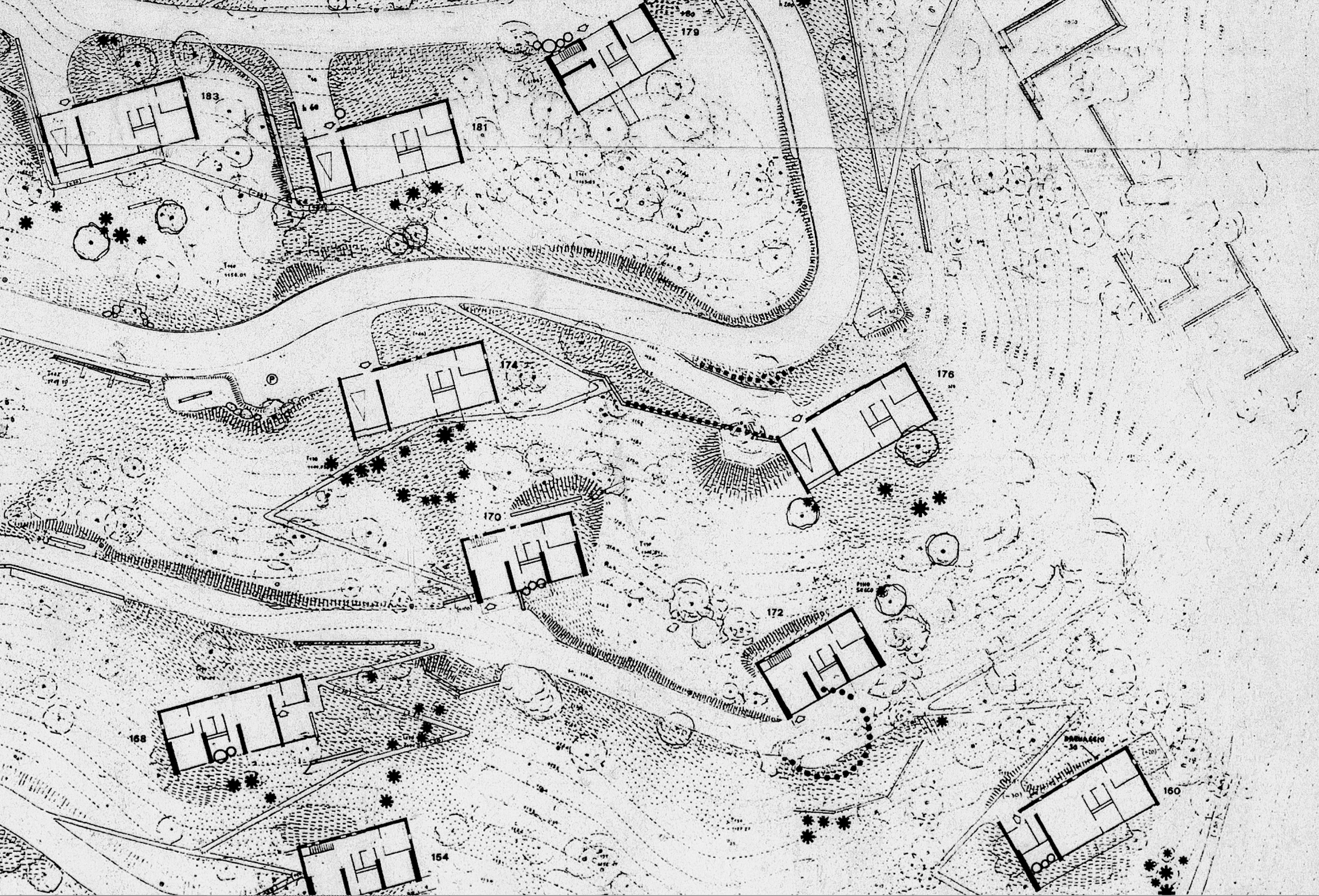
La seconda sezione, più consistente, contiene testi di autori che parlano delle loro opere architettoniche, tra cui emerge lo scritto di Alberto Ferlenga nel suo articolato intreccio capace di tenere insieme e fare operare riflessione teorica, analisi sul campo, progetto, disegno e parola. Tutta questa seconda parte è attraversata da contributi diversissimi, che danno perfettamente conto delle infinite forme con cui può darsi la dialettica contrappuntistica tra narrazione e costruzione, per di più in relazione al contesto montano e alle singole occasioni di progetto. Esattamente come era negli intenti di questo numero. Questo e il prossimo numero di ArchAlp sono parte di un programma annuale di ricerca e divulgazione nato in collaborazione tra l’Istituto di Architettura Montana e la Fondazione Courmayeur Mont Blanc sul tema dei nuovi immaginari sulla montagna contemporanea.
This issue of ArchAlp magazine reflects on the relationship between architectural design and its textual and narrative description. It attempts to explore this in several ways: designers telling the story of their own constructions or body of work; essayists and writers, not necessarily architects, narrating constructions that are particularly important and meaningful to them; or, as curated by the editorial team of the magazine, the republication of texts by 20th-century designers.
The goal of the writings – and thus of the entire issue – is to move beyond a mere functional and technical description of the building and reflect on the relational link between the constructed work and how it is described in text. The work and text are seen as a ‘microcosm’, allowing for reflection on the relationship of a single construction with the Alpine context, history, and techniques, highlighting a distinctive ‘idea of mountain architecture’.
However, it does not stop there. In recent years, much has been discussed about the relationship between dependence and autonomy in texts dedicated to architectural works by various modernist authors. What begins as a simple descriptive text of a project can transform into a theoretical operation or even a metatext that transcends the objects themselves to assert an independent dimension.
Tabù e tradizione nella costruzione montana by Carlo Mollino, published in 1954 and deliberately placed at the beginning of this issue, is considered one of the key texts, almost a manifesto, dedicated to Alpine architecture. It is interesting to observe how this writing creates images, metaphors, and syllogisms that, seventy years later, represent a kind of genetic heritage of the ways architecture looks at the mountains and their design – a text with inaugural significance, which establishes a ‘field’ with clear contents and boundaries.
The issue is organised into two sections. The first contains texts by writers, historians, critics, and architects discussing other people’s projects. The article by Enrico Camanni, a mountain writer, is remarkable in its recreation of the Stimmung and Hybris that characterised the modernity of the late 20th century in the context of Italian Alpine mass tourism. This is followed by the less conventional stories of the Haus Böhler by Heinrich Tessenow and the Capanna Monolina, along with the almost unpublished 1938 project by Gianni Albricci and Marco Zanuso.
The second, more substantial section includes texts by authors discussing their own architectural works. Alberto Ferlenga’s article stands out for its intricate approach that successfully combines theoretical reflection, field analysis, design, drawing, and words. The entire second section is permeated by a wide variety of contributions, perfectly capturing the infinite forms of the dialectic between narration and construction, especially concerning the mountain context and specific design examples of design, which is ultimately the underlying objective of this issue. This and the next issue of ArchAlp are part of an annual research and outreach program created in collaboration between the Institute of Mountain Architecture and the Courmayeur Mont Blanc Foundation on the topic of new imaginaries on contemporary mountains.